Residential property maintenance can entail high costs. This makes it all the more important to have precise knowledge of your tax options and benefits – also regarding repayment.
How you can save taxes with repayments
Save taxes with indirect repayments
The second mortgage can be paid off through indirect repayments by paying the annual instalments into pillar 3a. Once you reach retirement age, you can then use these 3a savings to pay off the entire second mortgage. The debt and the interest burden always remain the same during the repayment period. As a result, the amount of the deduction in your tax return does not change.
Another advantage is that the instalments paid into pillar 3a are also deductible from your taxable income. Indirect repayment may be particularly worthwhile in the case of higher income earners with a high marginal tax rate (see example). However, if the higher interest burden puts too much strain on your budget, you should opt for direct repayment.
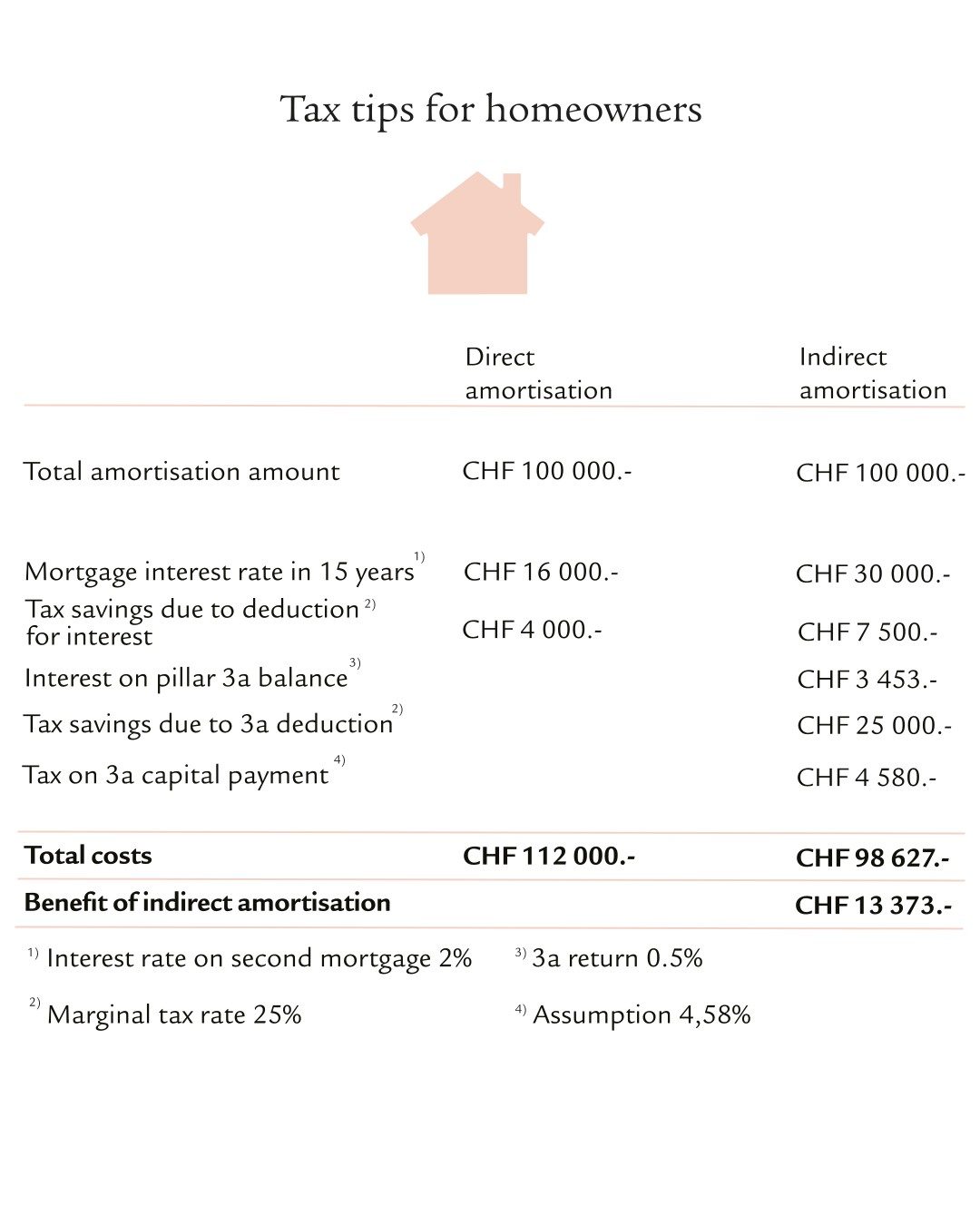

What can be deducted from taxes
Maintenance and renovation
In principle, all costs for the maintenance and renovation of your home are deductible from taxable income. This also includes value-preserving repairs, such as painting, gardening or renovation work.
Energy-saving measures
Investments in energy-saving measures in the building are also tax deductible. For example, if you install a photovoltaic or solar system, you can deduct the costs from your taxable income. Any plumbing and roofing costs incurred can be deducted as building maintenance.
Loan interest
In addition to maintenance costs, loan interest may also be deducted under Swiss tax law. This applies regardless of whether a mortgage or other interest-bearing loan was taken out when the property was acquired.
Conditions for tax deductions
Homeowners in all cantons of Switzerland can choose between flat-rate deduction or the deduction of actual costs. The flat rate is typically 10 to 20% of the imputed rental value or rental income. If you forego the lump-sum deduction and opt for the actual costs incurred, you must submit all invoices and receipts for deductible expenses to the tax authorities as supporting documents. If supporting documents are incomplete or missing, only the flat-rate deduction is permitted.
Save on taxes when renovating
The basic rule is that only renovation costs which maintain the condition of the property can be deducted in the tax return. Such value-preserving measures include, for example, replacing windows, installing new heating systems or repairing the façade. You cannot deduct value-adding work from your taxable income. This comprises additions that enhance the value of the property, such as a luxurious upgrade to the bathroom or an extension for a garage. However, these expenses are deductible from the taxable capital gain in the event of the property’s sale.
It’s a good idea to spread larger investments in value-preserving work over multiple tax assessment periods. For example, if renovations exceed half of your taxable income, divide them over two years. You can divide the work into several phases or spread renovations across years.








